
Flow testing on straight valves, right angle valves, and air release valves ensures fire protection systems perform effectively during emergencies. It verifies water flow and pressure meet safety standards. According to NFPA 25, regular inspections and testing identify issues, prevent failures, and ensure compliance. Reliable systems protect lives and property, making routine testing a non-negotiable safety measure.
Key Takeaways
- Testing straight valves often helps fire systems work well in emergencies.
- Use tools like flow meters and pressure gauges to check water flow and pressure correctly. This ensures safety rules are followed.
- Write down test results and maintenance to monitor the system and find problems early.
Preparation and Setup

Tools and Equipment for Straight Valve Testing
Proper tools and equipment are essential for accurate flow testing of straight valves. Technicians should gather all necessary items before starting the procedure to ensure efficiency and precision. Commonly required tools include:
- Flow meters for measuring water flow rates.
- Pressure gauges to monitor system pressure.
- Wrenches and screwdrivers for valve adjustments.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respirators.
- Data recording devices or logbooks for documenting test results.
Industry standards like API 607 and API 6FA provide guidelines for selecting appropriate tools for valve testing. These standards ensure that the equipment used meets safety and performance requirements. Adhering to these benchmarks guarantees reliable results and compliance with regulatory expectations.
Inspecting the Straight Valve and System Components
Before initiating the flow test, technicians must inspect the straight valve and related system components. This step ensures the system’s integrity and identifies potential issues that could affect test results. The inspection process includes the following tasks:
| Inspection Task | Description |
|---|---|
| External Inspection | Check for physical damage and ensure trim valves are in correct positions. |
| Intermediate Chamber | Verify there are no leaks. |
| Internal Inspection | Conduct annually during trip tests. |
| Strainers and Filters | Inspect every 5 years unless otherwise indicated. |
Additionally, technicians should verify the condition of manual valve actuators and pressure gauges. Ensuring all ancillary components, such as solenoid valves and pressure switches, are present and functional is equally important. These steps align with industry protocols to maintain system reliability.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance Before Testing
Safety and compliance are critical when performing flow tests on straight valves. Technicians must follow established guidelines to protect themselves and others during the procedure. OSHA’s safety standards emphasize the importance of proper respirator fit testing, which includes:
- Selecting an appropriate respirator model.
- Providing instructions on fitting and adjustment.
- Conducting user seal checks to confirm a secure fit.
- Prohibiting testing if facial hair interferes with the respirator seal.
Technicians should also wear PPE, including gloves and goggles, to minimize exposure to potential hazards. Following these safety measures ensures a secure testing environment and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Step-by-Step Testing Procedure
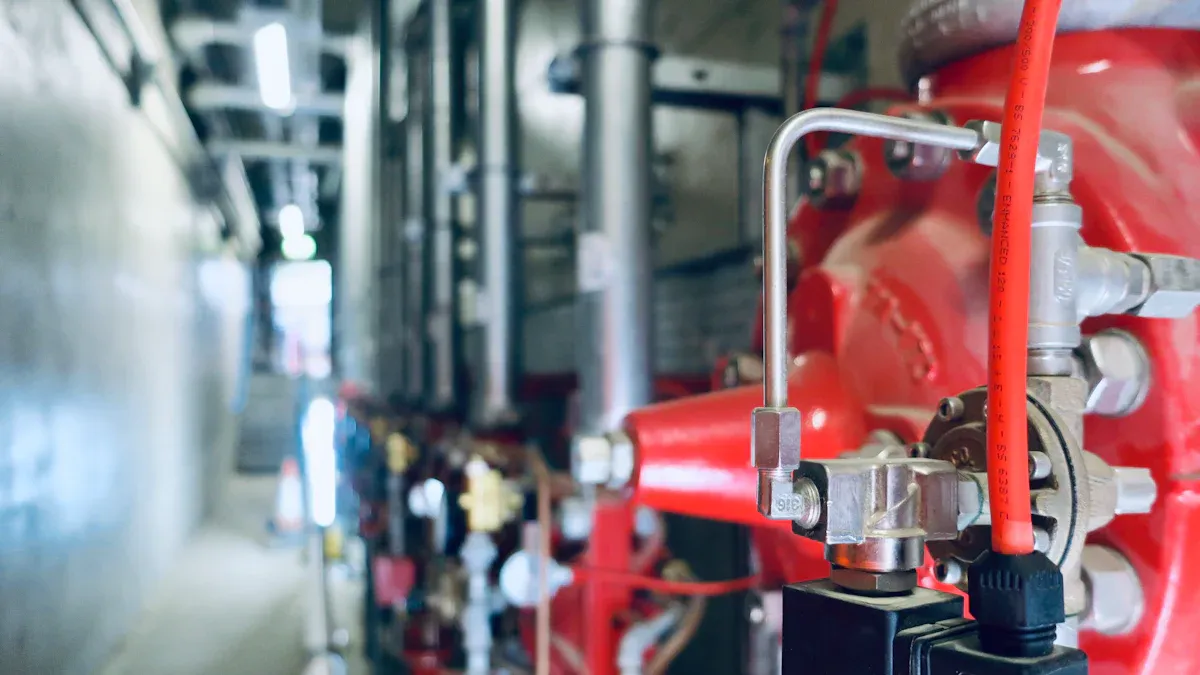
Opening the Straight Valve for Initial Flow
Opening the straight valve is the first step in the flow testing process. Technicians should ensure the valve is fully operational and free from obstructions before proceeding. Begin by slowly turning the valve handle to its open position. This gradual approach prevents sudden pressure surges that could damage the system or cause inaccurate readings. Observing the initial water flow helps identify any irregularities, such as blockages or leaks, that may require immediate attention.
During this step, technicians should monitor the system’s pressure gauge to confirm that the pressure remains within the expected range. If the pressure deviates significantly, it may indicate a malfunction in the valve or other system components. Addressing these issues early ensures the accuracy of subsequent measurements.
Tip: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling straight valves to minimize exposure to potential hazards.
Measuring Flow Rate and Pressure Accurately
Accurate measurement of flow rate and pressure is critical for evaluating the performance of a straight valve. Technicians should use calibrated instruments to ensure precision. The following table outlines commonly used instruments and their accuracy ranges:
| Instrument Type | Accuracy Range | Calibration Method |
|---|---|---|
| Deadweight Tester | 99.9% accuracy | Uses primary weight measurements based on NBS data; ideal for laboratory testing. |
| Portable Gauge Tester | 0.25% to 0.5% error | Uses a test gauge instead of weights; suitable for field applications. |
| Downhole Gauge (Ball Brothers) | 0.2% accuracy | Telemeters data to a chart/recorder; accuracy affected by data transfer method. |
| Electronic Recorders | 1.0% accuracy | Measures deflection of Bourdon tube mechanically; suitable for high-pressure applications. |
| Volumetric Prover Tank | N/A | Measures flow by timing liquid flow into a precisely marked tank; unaffected by fluid viscosity. |
| Piston/Ball Provers | N/A | Displaces a known volume of fluid; generates electrical pulses for precise measurement. |
Flow meters, such as Venturi tubes or ultrasonic meters, are also essential for measuring water flow. Regular calibration of these devices ensures reliable results. For example, Venturi tubes require periodic checks using manometers to verify pressure readings. Ultrasonic meters may need electronic recalibration to account for internal changes caused by corrosion or deposition.
Technicians should record all measurements in a logbook or digital device for later analysis. Consistent documentation helps track system performance over time and ensures compliance with industry standards.
Adjusting and Repeating for Consistent Results
Achieving consistent results often requires adjustments to the valve settings. Technicians should make incremental changes to the valve’s position while monitoring flow rate and pressure. This iterative process ensures the system operates within its optimal range. The following best practices support consistent outcomes:
- Calibrate testing equipment regularly to maintain accuracy.
- Verify the performance of instruments before each test.
- Clean and inspect equipment to prevent measurement errors.
If discrepancies persist, technicians should recheck the straight valve and associated components for potential issues. For example, worn-out seals or debris buildup may affect the valve’s performance. Addressing these problems promptly ensures the system functions as intended.
Note: Consistency in testing procedures not only improves reliability but also enhances safety by identifying potential system failures early.
Post-Test Actions
Recording and Analyzing Test Data
Recording and analyzing test data ensures the reliability of fire protection systems. Technicians should document flow rates, pressure readings, and valve performance during testing. This data serves as a reference for identifying trends and recurring issues. Maintenance requirements often increase as systems age, making detailed post-test documentation essential. Neglecting this step can lead to system failures, as revealed in postmortems of failed systems.
Standardized methods for data analysis improve accuracy and consistency. Projects like FlowCAP demonstrate the importance of automated data analysis by comparing it to expert manual gating. These approaches validate the need for precise recording and interpretation of flow test results. Technicians should use digital tools or logbooks to maintain organized records, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Restoring the System to Operational Readiness
Restoring fire protection systems to operational readiness involves several maintenance tasks. Technicians must verify that all components function correctly after testing. The following table outlines recommended protocols based on NFPA 25 standards:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Reference from NFPA 25 |
|---|---|---|
| Test supervisory signal devices | Annually | 13.2.8.2 |
| Operate control valves through full range | Annually | 13.3.3.1 |
| Test control valve supervisory switches | Semiannually | 13.3.3.3.5.1 |
| Flow test backflow preventers | Annually | 13.7.2.1 |
| Hydrostatic testing of piping | Every 5 years | 6.3.2.1 |
Technicians should inspect control valves, clean system components, and recalibrate instruments to ensure optimal performance. These steps restore the system to its original state, ready to respond effectively during emergencies.
Scheduling Regular Flow Tests for Straight Valves
Regular flow tests on straight valves are vital for maintaining system reliability. Industry best practices recommend the following strategies:
- Conduct periodic inspections to identify damage or wear.
- Implement cleaning protocols to prevent deposit accumulation.
- Replace diaphragms based on operational conditions and manufacturer guidelines.
- Calibrate automated mechanisms for accurate flow control.
- Maintain detailed logs of maintenance activities and inspections.
These strategies ensure consistent performance and extend the lifespan of straight valves. Scheduling tests at regular intervals helps technicians detect issues early, reducing the risk of system failures. Yuyao World Fire Fighting Equipment Factory emphasizes the importance of proactive maintenance to safeguard lives and property.
Flow testing plays a vital role in maintaining the reliability of fire protection systems. Regular testing ensures compliance with safety standards and identifies potential issues early. Key steps include inspecting valves, measuring flow rates, and restoring systems. The following table highlights testing frequencies recommended by industry standards:
| Standard | Frequency of Testing |
|---|---|
| AWWA | Every 10 years |
| NFPA | Every 5 years |
Routine testing safeguards lives and property effectively.
FAQ
What is the recommended frequency for flow testing straight valves?
Industry standards suggest testing straight valves every 5 years for compliance. However, Yuyao World Fire Fighting Equipment Factory recommends more frequent testing based on system usage and conditions.
Why is accurate flow rate measurement important?
Accurate flow rate measurement ensures the fire protection system delivers sufficient water during emergencies. It also helps identify potential issues, ensuring system reliability and compliance with safety standards.
Can technicians perform flow testing without specialized tools?
No, technicians require calibrated tools like flow meters and pressure gauges. These tools ensure precise measurements, which are critical for maintaining system performance and safety compliance.
Post time: May-05-2025

